In this tutorial, you will learn how to develop a Spring 4 MVC Hello world example. We hope this tutorial will give you a quick start with Spring MVC development using the latest Spring 4 Release.
Technologies used:
- Spring 4.0.4.RELEASE
- JDK 1.8
- Tomcat 7.0.53
- Maven 3.2.1
- Eclipse Java EE IDE ( Eclipse Kepler)
Maven Project Setup In Eclipse
Let us start with the creation of a Maven web project in Eclipse. A maven web project archetype will create all the necessary folder structures required for a web project. We assume that you have installed the Maven plugins for Eclipse.
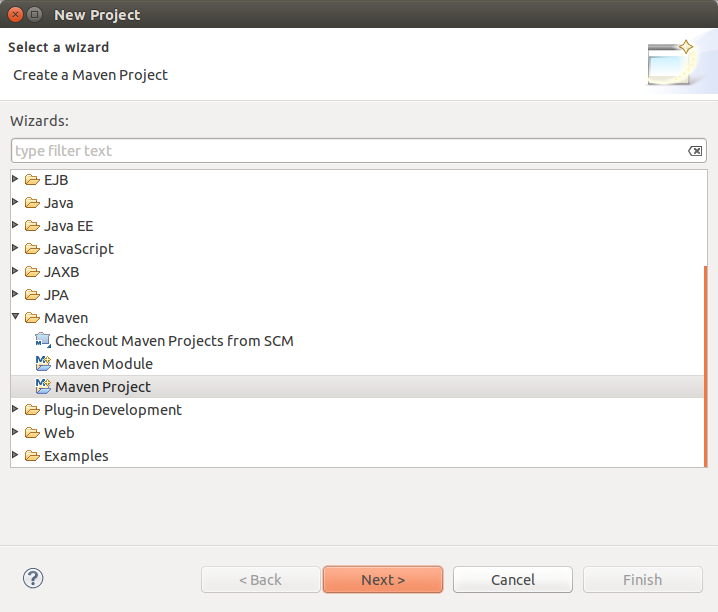
File -> New -> Other -> Maven -> Maven Project
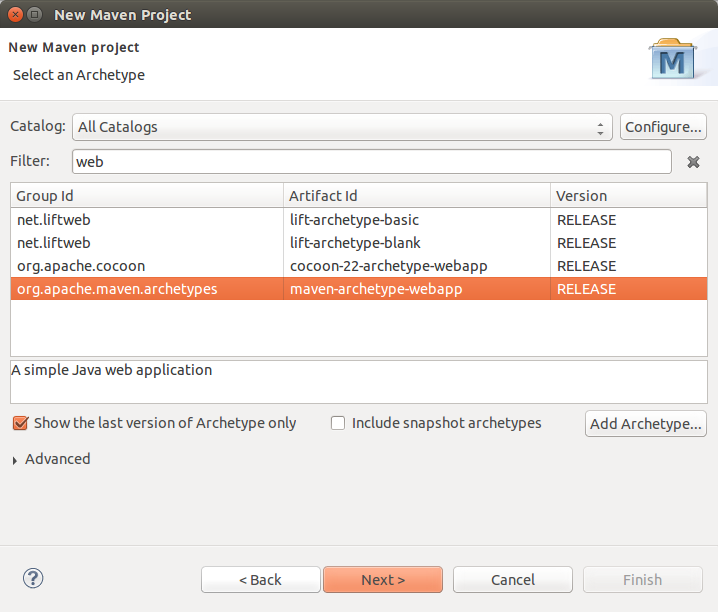
Click Next and Click Next again ( If you wish to change the default Workspace location, you may do so). On the next screen, you should pick the maven web app archetype. Refer to the screen below.
Click Next and provide the following values:
GroupId :com.happystudio ( you can change this according to your package structure)
Artifact Id: spring
Version: 0.0.1-SNAPSHOT
Click Finish to complete the Project Setup.
Once the project was created, you may get this error in index.jsp:
The superclass “javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet” was not found on the Java Build Path
You can solve it by Adding Apache Tomcat to your Java Build Path.
Reference: http://stackoverflow.com/questions/22756153/httpservlet-was-not-found
Spring Configuration
We now need to add the spring framework libraries as dependencies in Maven (pom.xml). For the sake of ease, we are going to define a maven variable to hold the spring framework version. If we need to change to a different spring release only this variable needs to be changed.
Dependencies – pom.xml
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.happystudio</groupId>
<artifactId>spring</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>Spring MVC Tutorial</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<spring.version>4.0.4.RELEASE</spring.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-web</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.11</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>Spring MVC Tutorial</finalName>
</build>
</project>
Spring Beans Configuration
We need a configuration file that holds the spring configuration information. In this tutorial, we will be using Spring’s auto-scan feature ( annotation) to detect and initialize beans. We can name this configuration file any name. We are using the name dispatcher-servlet.xml for this project. And put this file in webapp/WEB-INF/.
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc-4.0.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-4.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.happystudio.spring.controller" />
<bean
class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix">
<value>/WEB-INF/views/</value>
</property>
<property name="suffix">
<value>.jsp</value>
</property>
</bean>
</beans>
We have told spring to look at the package com.happystudio.controller for the beans and we have also told the framework that all views are kept under WEB-INF/views folder.
Web App Configuration
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.5"
xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee
http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_2_5.xsd">
<display-name>Spring MVC Tutorial</display-name>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>
org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet
</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>dispatcher</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/dispatcher-servlet.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<listener>
<listener-class>
org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener
</listener-class>
</listener>
</web-app>
Controller Development
From Spring 3 onwards, there exists excellent support for annotations. We will use annotations to mark our class as a controller in the standard MVC design. The HelloWorldController is a very simple controller that just echoes a message. It takes a parameter and just echoes it.
package com.happystudio.spring.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
@Controller
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(
@RequestParam(value = "name", required = false, defaultValue = "World") String name,
Model model) {
model.addAttribute("name", name);
return "helloworld";
}
}
Please note the use of @Controller and @RequestMapping . The URL takes a parameter with the name “name”.
Hello World View in webapp/views/helloworld.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=utf-8" pageEncoding="utf-8"%>
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Spring MVC Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello : ${name}</h1>
</body>
</html>
We can generate a War file and deploy that to a webserver to test the application. In Eclipse, right-click the project and Click Run As –> Maven Install. This will build the project and create a war file in the target folder. In the case of this example, the file will be spring.war
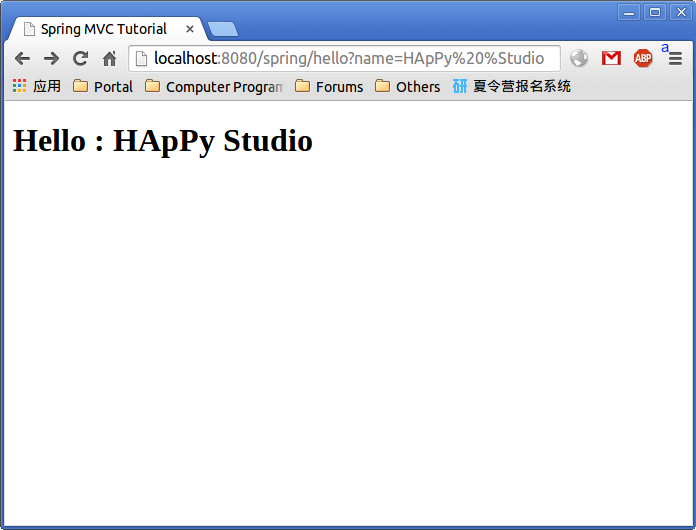
You can get a greeting by visiting http://localhost:8080/spring/hello/?name=HApPy%20%Studio
The Disqus comment system is loading ...
If the message does not appear, please check your Disqus configuration.